Ensuring the safe transport and handling of dangerous goods is critical in preventing accidents and protecting both people and the environment. Hazardous material codes play a vital role in the process by providing standardised guidelines for classifying, packaging and documenting hazardous materials. Among the various international regulations, the International Maritime Dangerous Goods (IMDG) Code stands out as a key framework for maritime transport.
What Are Hazardous Material Codes?
Hazardous material codes are a set of regulations and guidelines designed to safely manage the storage, handling, and transport of dangerous goods. These codes categorise materials based on their potential hazards, such as flammability, toxicity, or corrosiveness, and provide specific requirements for labeling, packaging, and documentation to ensure safe handling.
Overview of the IMDG Code
The IMDG Code was developed by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) to enhance the safe transportation of dangerous goods by sea. Since its inception in the 1960s, the IMDG Code has been regularly updated to incorporate new safety standards and technological advancements. The code aims to prevent marine pollution and ensure the safety of ships and their crews by standardising practices across the international waters.
Structure and Classification of the IMDG Code
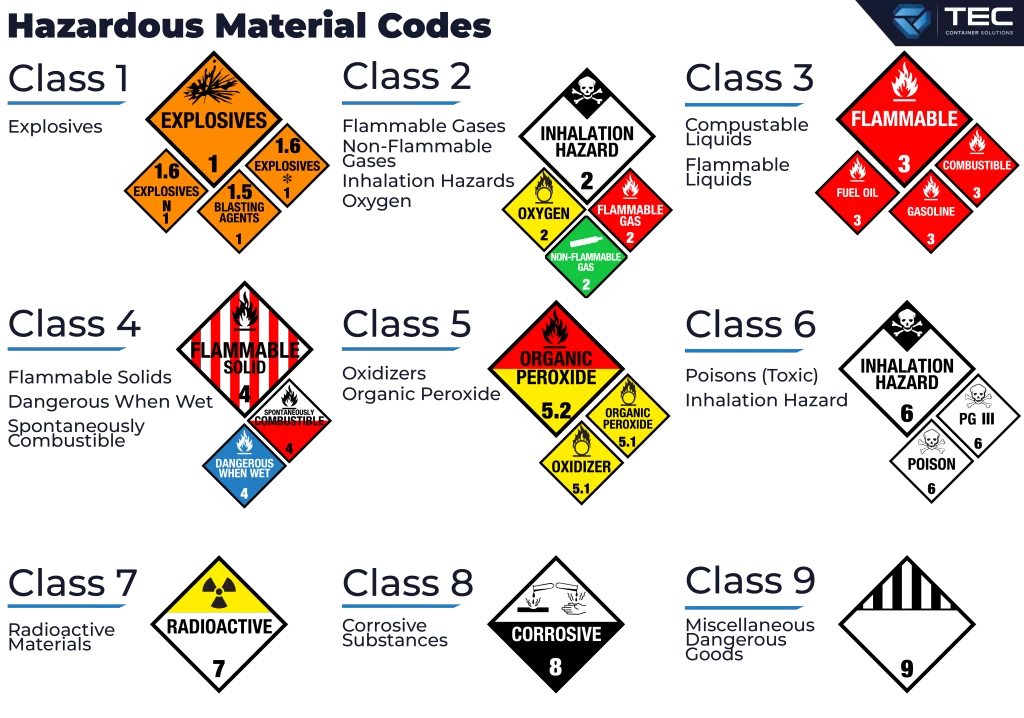
The IMDG Code classifies hazardous materials into nine distinct classes, each representing a different type of hazard:
- Class 1: Explosives
- Class 2: Gases
- Class 3: Flammable Liquids
- Class 4: Flammable Solids
- Class 5: Oxidizing Substances and Organic Peroxides
- Class 6: Toxic and Infections Substances
- Class 7: Radioactive Materials
- Class 8: Corrosive Substances
- Class 9: Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods
Each class has specific labelling and packaging requirements to ensure that the hazards are clearly communicated and managed. The IMDG Code also outlines detailed documentation procedures, including the Dangerous Goods Declaration and the Container Packing Certificate, which are essential for compliance and safety.
Importance of Compliance with Hazardous Material Codes
Compliance with hazardous material codes is not just a legal requirement but a critical component of safety management. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including fines, legal action, and accidents that endanger lives and the environment. Ensuring adherence to these codes helps mitigate risks, protect personnel, and maintain operational integrity.
Practical Tips for Handling Hazardous Materials
To safely handle and transport hazardous materials, businesses should implement the following practices:
- Proper training: Ensure that all personnel involved in handling dangerous goods receive adequate training and certification.
- Accurate documentation: Maintain precise and up-to-date documentation for all hazardous materials.
- Adequate packaging: Use appropriate packaging materials and methods to prevent leaks and spills.
- Clear labeling: Clearly label all hazardous materials according to the relevant codes and standards.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits and inspections to ensure compliance with all safety regulations.
Understanding and adhering to hazardous material codes are essential for ensuring safety and legal compliance in the transport and handling of dangerous goods. By following the guidelines set forth in the IMDG Code and other relevant regulations, businesses can protect their employees, the environment, and their operations from the risks associated with hazardous materials.






